What is compatibility tests and how are they performed?
- What is a compatibility test and how are they performed?
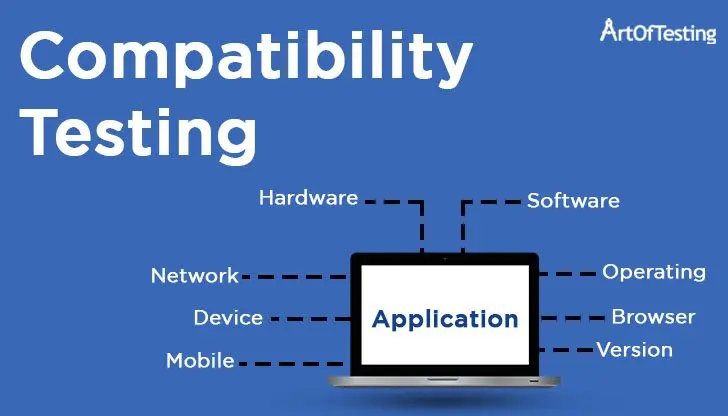
Compatibility testing is a type of software testing that evaluates how well a software application performs across different environments, configurations, devices, browsers, operating systems, and network conditions.
Performing compatibility testing involves the following steps:
1. Identify Target Environments:
- Determine the range of platforms, devices, browsers, operating systems, and network conditions that the application should be compatible with.
2. Create a Test Matrix:
- Create a matrix that maps the combinations of environments, configurations, and devices to be tested.
3. Testing Tools and Infrastructure:
- Use testing tools and frameworks that can simulate various environments and configurations.
- Tools like virtual machines, emulators, and cloud-based testing services can be used to set up and test different combinations.
4. Functional Testing:
- Verify that the application's core functionalities work as expected across different environments.
- Check for any inconsistencies or variations in behavior across platforms.
5. UI and Layout Testing:
- Ensure that the user interface (UI) elements and layouts display correctly on different devices and screen sizes.
- Test for responsive design and adaptability to various resolutions.
6. Browser Compatibility Testing:
- Test the application's compatibility with different web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Internet Explorer).
- Verify that the UI elements, functionality, and behavior remain consistent.
7. Operating System Compatibility Testing:
- Test the application across different operating systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS).
- Check for platform-specific issues that might affect functionality.
8. Device Compatibility Testing:
- Test the application on different devices, such as desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Verify that touch interfaces, screen sizes, and device-specific features work correctly.
9. Network Compatibility Testing:
- Test the application's performance under various network conditions, including different connection speeds and stability levels.
10. Security and Privacy Testing:
Ensure that the application maintains security standards and data privacy requirements across different environments.
- Localization and Internationalization Testing:
- Verify that the application works well with different languages, cultures, and regions.
- Accessibility Testing:
- Ensure that the application is accessible to users with disabilities across different platforms.
- Documentation and Reporting:
- Document the test scenarios, findings, and issues encountered during compatibility testing.
- Report any inconsistencies, bugs, or deviations from the expected behavior.
Comments
Post a Comment